
Cloud Engineer
AWS Strands Agents: The Simple Path to Your Own AI Agents
Why AI Agents are relevant right now
How Strands Agents work
The Strands Agents SDK is an open-source framework from AWS that makes it significantly easier to develop AI agents with Python. It is modular, lightweight, and designed to cover everything from simple prototypes to complex production scenarios. Instead of relying on rigid process models, Strands follows a model-driven approach. The large language model takes on the role of orchestrator: in an agent loop, it analyses es the task, selects suitable tools, executes them, and then evaluates the result. This creates a flexible system that can adapt to new situations without requiring all processes to be manually predefined.
One of Strands’ core strengths lies in its tools. These are small functional building blocks that give an agent specific capabilities, such as reading a file, retrieving data from an API, or calculating key metrics. Such tools can be easily defined by developers or taken from a growing community library. Additional APIs and services can also be integrated via the Model Context Protocol. Execution can be sequential when one result builds on another, or parallel when multiple steps make sense simultaneously.
Strands Agents supports both simple scenarios with a single orchestrator and complex multi-agent setups in which several agents collaborate. One example is a cost analysis agent working alongside an incident response agent: when unusual expenses occur, it not only issues a warning but also helps narrow down the cause. Another major strength is its close integration with the AWS environment, which enables seamless deployment to services such as Lambda, Fargate, or EKS.
To ensure agents work reliably, Strands Agents provides mechanisms for context and state. A conversation history ensures that information from previous interactions is considered. Important variables can also be stored in the agent state. Structured outputs make it possible to enforce that an agent delivers results in a defined format, which simplifies integration into existing systems.
Another key feature is observability. With each run, agents collect telemetry data, traces, and logs. These can be evaluated using common standards such as OpenTelemetry, giving developers and operators full visibility into costs, behaviour, and quality. In addition, the SDK provides security features such as Bedrock Guardrails, which filter out unwanted content and protect sensitive data.
Once agents are equipped with the necessary security and monitoring features, the next step is deployment. This often starts with a local test run. As soon as an agent works reliably, it can be deployed to AWS services such as Lambda, Fargate, or EKS with ease. This makes the transition from initial idea to productive use only a small step. How these features can be applied in practice is demonstrated in the following example from the field of cloud cost management.
Practical Example: FinOps Agent
A practical use case for Strands Agents is cloud cost management. Here, a FinOps agent helps companies detect anomalies at an early stage, narrow down their causes, and derive concrete actions.
While AWS already offers a managed service for cost anomaly detection, this example demonstrates how a custom agent built with Strands Agents can be flexibly adapted and integrated into existing workflows. The focus is less on pure functionality and more on ease of creation and the ability to extend the agent with custom tools.
In the demo, the agent reads data from a simplified CSV file. In a real-world scenario, the agent could be directly connected to the relevant AWS services. For example, it could use the AWS Cost Explorer API to retrieve current expenses, compare them with defined budget limits, and automatically send notifications or even trigger preventive actions in the event of anomalies.
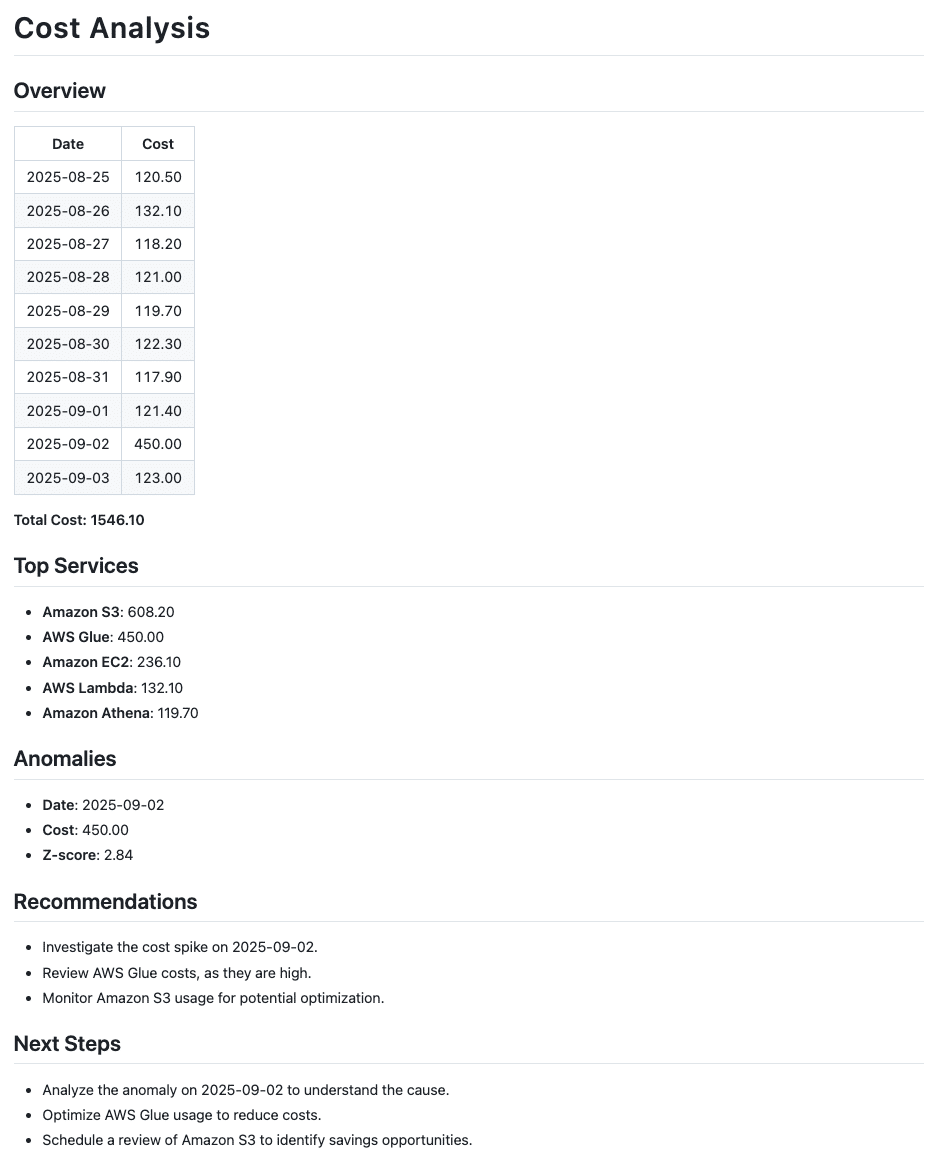
- Create Agent: In the first step, an agent is created with the desired model and tools. In this example, the tools include functions for reading the CSV file and detecting cost anomalies.

- Define Prompt: Next, the agent is given a clear prompt that specifies the task it should perform. In this case, the task is to analyse cloud costs and identify unusual patterns.

- Understand Output: Finally, the result shows how the agent processes the data and presents it in a structured output. This makes anomalies visible and derives initial recommendations that can be integrated into an existing FinOps setup.
Conclusion and Outlook
The AWS Strands Agents SDK provides an ideal entry point for experimenting with AI agents and gaining initial hands-on experience. As a relatively new framework, Strands Agents is lightweight and flexible. Thanks to rapid development and early community feedback, it is particularly well suited for prototyping and initial production use cases.
In addition to Strands Agents, there are other frameworks for building AI agents, some of them more established, such as LangChain, CrewAI, or LlamaIndex. Which framework is best suited in a given case always depends on the intended use case. This blog post, however, deliberately focuses on Strands Agents.
With its model-driven approach, straightforward extensibility through tools, and support for multi-agent architectures, Strands Agents opens up a broad range of possibilities. This is complemented by built-in features for observability and security, which are essential for practical deployment. As a result, the SDK provides a solid foundation for a wide variety of use cases and clearly points to the potential of future developments.
For those who want to dive deeper, the official documentation with practical examples and demo scenarios is available at strandsagents.com. The full source code is also accessible in the GitHub-Repository verfügbar.



